Milk is a rich source of essential nutrients that are required for our body, especially optimal heart functions. It is rich in high-quality protein and is an excellent source of vitamins and minerals such as calcium, vitamin B12 and riboflavin.
Benefits of drinking milk:
- Milk is one of the best sources of calcium for the body
- Milk is rich in Vitamin D that helps the body absorb calcium
- Proper calcium intake contributes to strong and healthy bones
- Drinking milk provides other benefits such as healthy teeth and nerves
Now that you know milk brings a lot of goodness with it, let’s look at the types of milk generally consumed.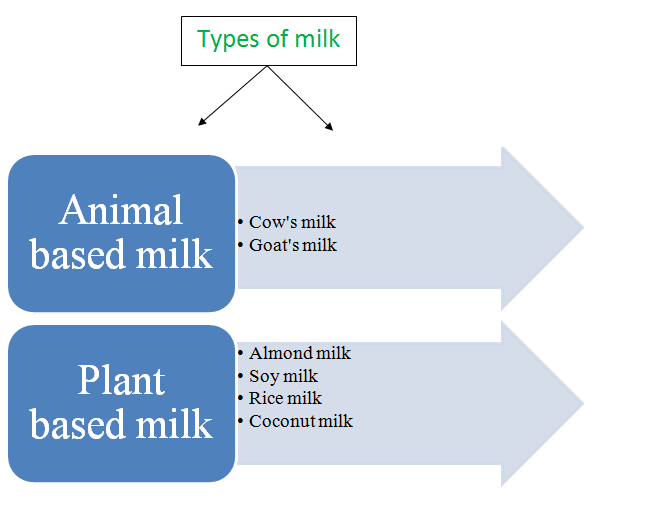
Cow’s milk
- Cow’s milk comes in various types and brands (Table 1)
- Whole milk can provide essential proteins, extra calories from fats, as well as vitamins and minerals for infants and older adults
- It is high in calcium, which is the key for healthy bones
- It is less expensive and widely available in grocery stores and convenience stores
Cons of cow’s milk:
- Whole milk is high in saturated fat as well as cholesterol as it’s animal based
- Milk is a common cause of food allergy (allergy to milk protein)
- Many people lack the enzyme to digest lactose (milk sugar). This is called lactose intolerance, which causes bloating, gas, and diarrhoea.
Table 1. Locally available cow’s milk brands
| Brand | Type of milk | Colour of packet | Fat ( %) |
| Aavin | Toned
Double toned Standardised Full cream |
Blue
Magenta Green Red |
3
1.50 4.50 6 |
| Heritage
|
Toned
Double toned Full cream Standardised Golden Cow Slim Family toned |
Green
Pink Orange Blue (dark) Yellow Violet Blue (light) |
3
1.0 6 4.5 3 0.1 3 |
| Mother dairy | Toned
Standardised Full cream |
Blue
green Orange |
3
4.5 6 |
| Amul
|
Toned
Double toned Premium Full cream |
Blue (dark)
Blue (light) Red Pink |
3
1.5 7 6 |
| Cavin’s | Toned
Standardised Full cream |
Magenta
Blue Orange |
3
4.5 8 |
| Arokya | Toned
Double toned Standardised Full cream |
Blue
Pink Violet Orange |
3
1.5 4.5 6.5 |
| Jersey
|
Toned
Double toned Skimmed Full cream |
Green
Orange Pink Red |
3
1.5 4.5 6.5 |
Goat’s milk
- This milk is easily digestible by humans
- It is rich in calcium and tryptophan level which is an essential amino acid
- Goat’s milk contains selenium, an essential trace mineral that supports the immune system
Cons of goat’s milk:
- Goat milk is deficient in folic acid and vitamin B6 and B12 which are all essential for growth and well-being
- Hence exclusive goat milk diet in infants and young children can be dangerous
- It is expensive compared to cow’s milk
Almond milk
- It is low in calories and contains no saturated fat
- It is a good source of vitamin A and can be fortified to be a good source of calcium and vitamin D
- It is vegan and naturally lactose-free
Cons of almond milk:
- It is not a good source of protein
- It may contain carrageenan, which may cause digestive issues in some people
- It affects thyroid hormone levels
Soy milk
- It is a good source of protein, vitamin A, vitamin B12, potassium, and isoflavones, plus it can be fortified with calcium and vitamin D
- The fat content in soy milk is good for the healthy heart
- It contains very little saturated fat
Cons of soy milk:
- Soy is a common allergen for both adults and children
- Too much soy may be a problem for people with thyroid conditions
- Too much soy of any kind in the male diet can cause infertility problems
Rice milk
- It is the least allergenic of milk alternatives
- It can be fortified to be a good source of calcium, vitamin A, and vitamin D.
- Rice milk is naturally sweeter than other milk alternatives
Cons of rice milk:
- It is high in carbohydrates, so it’s the least desirable choice for people with diabetes
- It is not a good source of protein
- Eating too much of a rice product may pose a health risk for infants and children due to inorganic arsenic levels
Coconut milk
- It is highly nutritious and rich in fibre, vitamins C, E, B1, B3, B5 and B6 and minerals including iron, selenium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and phosphorous
- It rarely causes allergies
- Coconut milk is lactose-free so can be used as a milk substitute by those with lactose intolerance
Cons of coconut milk:
- High amounts of saturated fat in coconut may contribute to weight gain
- It is not a good source of protein
- Excessive intake of coconut milk can lead to cardiovascular diseases
Conclusion:
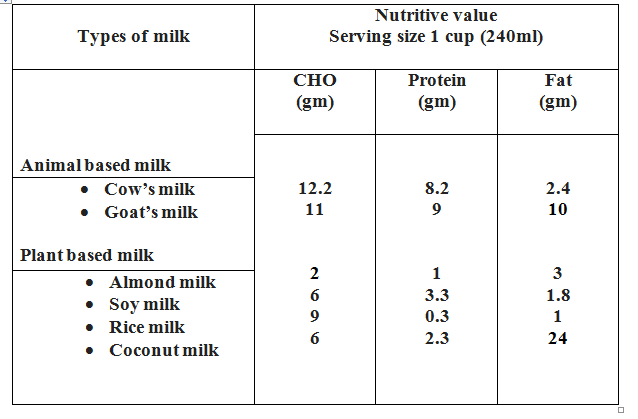
While milk comes in various types and strengths, there is no one size fits all when it comes to ideal milk. The table below gives the nutritive value of some commonly used milk types.
Toned (also known as skimmed or low fat) milk is suitable for children and adults; it has many important health benefits including its ability to build strong bones and teeth, boost the immune system, protect the heart, prevent diabetes, eliminate inflammation, aid in weight loss and help stimulate growth. Pasteurised milk is superior to raw milk as it is microbe-free and ready to drink.
The recommended daily allowance of calcium varies by age and gender. From ages 19 to 70, men should get 1,000 milligrams of calcium, and 1,200 milligrams if they are 71 and older. Women between the ages of 19 and 50 should get 1,000 milligrams of calcium a day, and 1,200 if they are 51 and older.
Make milk a part of your every day diet and enjoy good health!