Worldwide, 15 million people suffer a stroke each year of which one‐third die and one‐third are left permanently disabled. As a dietician focusing on the prevention and rehabilitation of lifestyle diseases, let me break down some important facts about stroke and it’s prevention.
What is stroke?
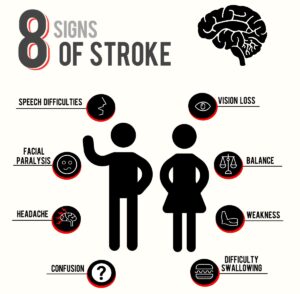
Stroke is a medical emergency that occurs due to obstruction of blood flow to the brain. Without proper blood flow, the brain cells fail to work and may even die and this causes serious symptoms such as inability to talk, walk and see and often death. Symptoms of stroke include the following sudden changes – numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg, usually on one side of the body, confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding, visual disturbances, dizziness and/or loss of balance.
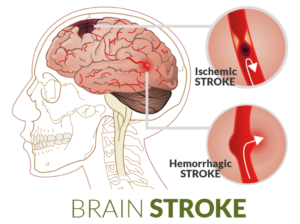
What are the types of stroke?
There are two main types of stroke namely ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot interrupts the blood flow to the brain. The blood clot is often due to atherosclerosis – a buildup of fatty deposits on the inner lining of a blood vessel. An ischemic stroke can be embolic, meaning the blood clot travels from another part of your body to your brain. A hemorrhagic stroke results as a blood vessel in your brain ruptures or breaks, spilling blood into the surrounding tissues.
It is important to note that stroke is a risk factor for heart disease and people who have had a heart attack have twice the risk of occurrence of stroke.
What are the risk factors for stroke?
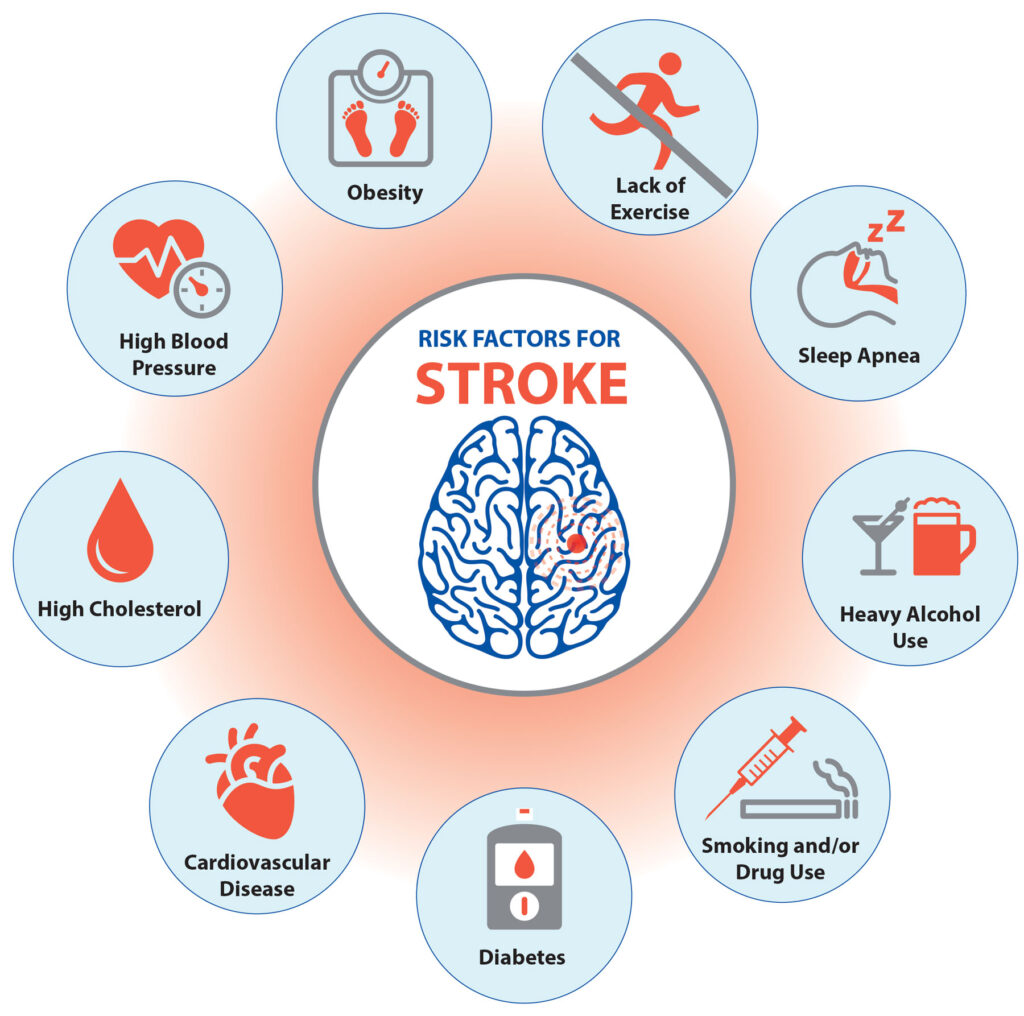
Stroke and heart attack are the two major non-communicable (non-infectious) diseases or cardiovascular diseases threatening the world today and have many commonalities. Both are vascular events that involve the blood vessels and the arteries in particular. Both conditions can lead to death in a matter of seconds to minutes. And both diseases are caused by the same lifestyle and metabolic risk factors listed below:
• High blood pressure
• Abnormal cholesterol
• Diabetes
• Unhealthy diet
• Sedentary lifestyle
• Obesity
• Smoking
• Excessive alcohol intake
• Severe mental stress
• Family history
• Atrial fibrillation (abnormal heart rhythm)
How to eat healthy to prevent stroke? A recent study conducted in nine European countries with a total of 4,18,329 participants has concluded that adequate daily consumption of fruits, vegetables, dietary fibre and dairy products reduces the risk of stroke and that too much red or processed meat consumption increases the risk of stroke. This study also shows that too much sodium (salt) in diet is associated with a higher risk of stroke, while improving potassium intake through fruits and vegetables is protective against stroke.
We also have solid scientific evidence to show that healthy eating habits and a balanced diet reduce the risk of hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and heart diseases.
There are some major food items that need to be considered while planning a healthy diet:
Red meat – meat is a major source of saturated fat, which could contribute to atherosclerosis and thus higher risk of stroke
Whole grains – whole grain products such as cereals and millets are rich in dietary fibre, and help in reducing the chances of stroke and it’s severity
Fruits and vegetables – fruits and vegetables are rich in anti-oxidants, which reduces free radicals in our body. They provide various micronutrients including potassium and folate. Potassium helps to reduce blood pressure while higher folate intakes may lower plasma homocysteine concentrations, and thereby reduce stroke risk. Fruits and vegetables are also a major source of dietary nitrates which have blood pressure lowering and blood vessel protective properties. Eating at least 5 cups of fruits and vegetables every day is the best thing we can do to keep stroke at bay
Dairy products – Dairy based foods, particularly low fat milk and low fat milk products like cheese, yogurt and paneer are rich sources of calcium, along with potassium, which can help to control blood pressure while keeping cholesterol within normal limits
There is a link between blood cholesterol levels and stroke. Saturated fat (unhealthy fat) found predominantly in animal organs (brain, liver, kidneys) and red meat (beef, veal, pork) are unhealthy and should be avoided while the healthy unsaturated fat found in fish, chicken and turkey breast can be included in our diet. Egg has a combination of proteins, fats and minerals and can be consumed in moderation.
Minimize the use of highly processed, preserved or packaged and frozen products as they are high in calorie and contain a lot of unhealthy saturated fat
It is important to read the labels of the products and to choose the ones that contain 0% transfat, low fat and no added sugar
What else should we do to prevent stroke?
1. High blood pressure is one of the biggest contributors to the risk of stroke in both men and women. Monitoring and maintaining optimal blood pressure (120/80 mmHg) helps to reduce the incidence of stroke. Also reducing salt intake to 1-2 grams (about a teaspoon) a day is a proven way to keep blood pressure under control and prevent heart attack and stroke.
2. Obesity as well as it’s complications are linked to stroke. Try to maintain a healthy normal weight to prevent occurrence of stroke
3. Regular exercise is extremely important to keep all the risk factors mentioned above under control. In fact, exercising everyday for about 30 minutes has the maximum benefits on all our organs and systems.
4. Elevated blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels over time that might result in clots, more likely to form inside them. Keeping your blood sugar under control through a healthy lifestyle and medications (if necessary) will help prevent stroke, heart disease, kidney failure and several other ailments.
5. Quit smoking and alcohol consumption that are direct risk factors of stroke and heart diseases
6. Atrial fibrillation is a form of irregular heartbeat that causes clots to form in the heart. Those clots can then travel to the brain by dislodging, resulting in an embolic stroke. If you have atrial fibrillation, get appropriate treatment at the earliest.
Too many people ignore the signs of stroke because they are unaware or unable to relate the symptoms to a serious underlying medical emergency. Now that you are aware what stroke is and how it can be prevented, you should become an ambassador of stroke prevention in your community.
If you choose a
well-balanced healthy diet, placing emphasis on natural, whole, and unprocessed
foods, and if you exercise regularly and keep all your risk factors under
control, you can protect yourself from stroke, heart attack and
other chronic ailments like dementia, cancer and lung disease.










