Would you like to understand ‘sugar’ better? While you might know that sugar is really sweet and enhances taste did you know that it can be dangerous too? Let me take you through some basic facts about sugar before seeing the health hazards of this sweet ingredient…
Sugars are broadly grouped into simple and complex sugars, and natural and added sugars.
Simple Sugars
Simple sugars are carbohydrates that are quickly absorbed by the body to produce energy. These sugars are present in both natural and processed foods. Natural foods that contain simple sugars include fruits, vegetables and milk products. Processed foods often have simple or refined sugars added to improve flavour. Examples of refined-sugar foods include candy, cakes, syrups, fruit juices and carbonated beverages.
Complex Sugars
Complex sugars are complex carbohydrates that take a longer time to digest as they are packed with fibre, vitamins and minerals. Examples are cereals, legumes, whole wheat pasta and vegetables.
Natural sugar
Natural sugar is naturally occurring, which makes them healthy. There are two types of natural sugars.
- Fructose – it is found in fruits
- Lactose – it is found in dairy products. These nutrients help to stabilize your blood sugar levels, which prevents you from feeling hungry soon after eating.
Added sugar
Added sugars are sugar carbohydrates added to foods and beverages during their processing. This does not include naturally occurring sugars such as those in milk and fruits. It provides empty calories that are of no benefit to your body. Examples are candy, cake, soft drinks, ice cream and other desserts. Consuming too much added sugar is a health hazard!
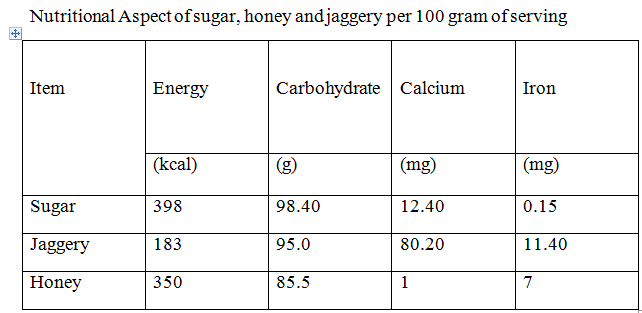
Sugar, honey and jaggery are the commonly used sweetening agents added to beverages and foods to increase palatability. The crystallised sugar we all keep in our kitchen shelves is made up of glucose and fructose. It’s a source of energy providing 4 kilocalories per gram. Jaggery is made from sugar cane juice after processing it and is a fair source of iron. Honey is the golden coloured syrup made by bees from the nectar of flowers. It also consists of glucose and fructose.
How much sugar can be consumed on a daily basis?
While theoretically, a normal healthy adult can consume 24 grams (or) 6 teaspoons per day, research reveals that minimal or zero added sugar is best for our health. Diabetic patients, however, have a reduced ability to metabolise sugar and should strictly avoid all forms of added sugar.
How many calories does one teaspoon of sugar contain?
Amount – 1tsp (4.2g)
Calories – 16 kcals
Carbohydrate – 4.2 g
Health risks of eating too much sugar
Sugar, an instant source of energy, can lead to multiple health problems if consumed in large quantities: weight gain, fatty liver disease, diabetes, hypertension, heart attack, stroke and kidney failure are some of the common ailments caused by this sweet substance.
Artificial sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners, also referred to as sugar substitutes, are used to replace sugar in foods and beverages. Sucralose, aspartame and saccharin are the mostly purchased artificial sweeteners, especially by diabetic individuals. We will look at these agents in depth in a future blog post, but it is apt to say that their use should be minimised keeping in mind their harmful side effects.
So, here are some tips to cut down on sugar in your daily diet:
- Instead of adding sugar to cereal or oatmeal, add fresh fruits (try bananas, pomegranate or berries) or dried fruit (raisins, cranberries or apricots).
- If you consume tea, coffee or milk with added sugar, try alternatives like green tea, black coffee and unsweetened milk.
- Instead of adding sugar in recipes, use extracts such as almond, vanilla, orange or lemon.
- Enhance the taste of foods with spices instead of sugar; try ginger, allspice, cinnamon or nutmeg.
- Compare the sugar content of different foods and choose the lower sugar and calorie option.
“ Eat less SUGAR;
You’re SWEET enough already”