All of us breathe unconsciously each second of our lives but can you just imagine what it would be like if our breathing itself is a problem. So in this post we are going to see how to proceed if disease affects our lungs (the medical term for lung is pulmo).
Rehabilitation or rehab means the act of restoring something to its original state. I would like to introduce the importance & effects of pulmonary rehabilitation, which simply means restoring the lungs to their original state.
Lung is the source of oxygen to our body; it is the key to our life. So, if disease affects our lungs what will happen to our body? The overall quality of life & function of our body reduces.
Any abnormality in the lungs that prevents it from working properly can lead to lung disease. And when the disease is present for more than 6 weeks, it is called chronic lung disease. Examples are chronic bronchitis, asthma, bronchiectasis and interstitial lung disorders.The main symptom of chronic lung disease is difficulty in breathing or breathlessness; the others are cough, excessive sputum production, tiredness and pain in the chest. Chronic lung disease is a major cause of morbidity and mortality across the world. By the year 2020, it is estimated that chronic lung disease will be the 5th most burdensome disease and 3rd leading cause of death worldwide. According to a World Health Organization report, the prevalence of this disease ranges between 4% and 20% among Indian adults. However, lack of awareness tends to underestimate prevalence and progression of chronic respiratory conditions.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation is an essential component in the management of individuals with chronic lung disease.It is an important modality and adjunct to other therapies such as medication and oxygen supplementation in men and women diagnosed with these conditions.
of individuals with chronic lung disease.It is an important modality and adjunct to other therapies such as medication and oxygen supplementation in men and women diagnosed with these conditions.
Members of the team
It is a multi-disciplinary approach and involves a physician, physical therapist, occupational therapist, respiratory therapist, social worker, psychologist and dietician.
Goals of rehabilitation:
- Preserving optimal lung function
- Improving functions of daily living
- Improving health-related quality of life
- Reducing symptoms
- Preventing recurrent exacerbations
People who undergo pulmonary rehab report the following benefits:
-
- Able to do more of daily activities
- Have less puffing and panting
- Feel an improvement in muscle strength
- Able to do more exercises with ease
- Feel less anxiety and depression
- Get an overall positive feeling about life
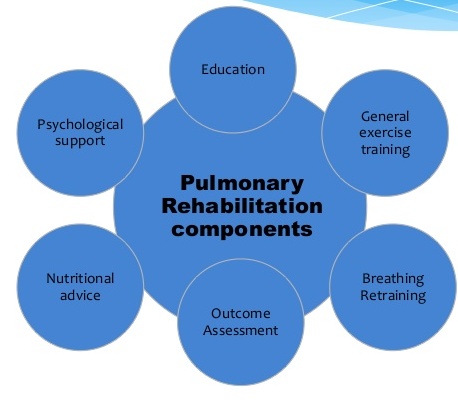
Components of pulmonary rehabilitation
1. Assessment
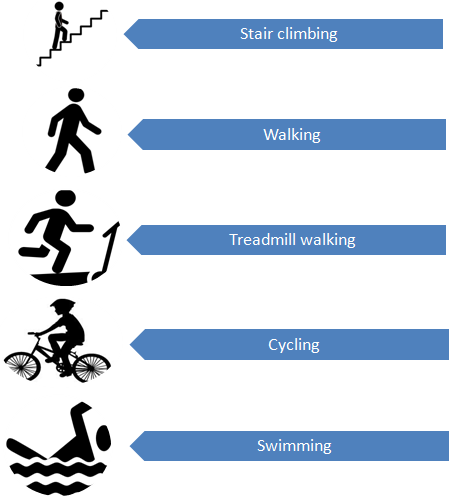
2. Exercise
3. Education /Training
4. Nutritional supplements
5. Psychological intervention
6. Vocational Training
Duration
A 10-12 week rehab program with 2-3 sessions per week with the rehab team will usually start producing obvious health benefits. The program will be tailored to the specific needs of the individual. For long term effects patients can continue with a maintenance program.
The education and counseling during the rehab program will help individuals in the following ways:
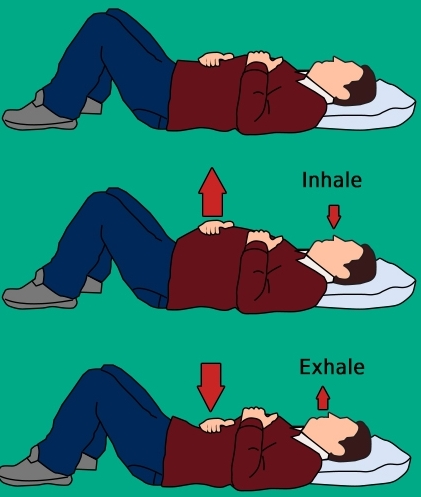
- Reduce and control breathing difficulties
- Understand the medical condition affecting their lungs, it’s treatment options, and coping strategies
- Reduce dependence on healthcare professionals and costly medical interventions
- Maintain healthy behaviours such as smoking cessation, good nutrition, stress management, and adequate exercise
It’s not the end to rest, it’s a NEW BEGINNING with pulmonary rehab