Health refers to physical, mental and social well being, as defined by the World Health Organization. Nutrition plays an important role in preserving health in all age groups, and more so in the elderly. If you are in your 60s, 70s and beyond or caring for someone who is 60 plus, you should read this post to understand the age-related barriers to healthful nutrition and the ways to overcome them.
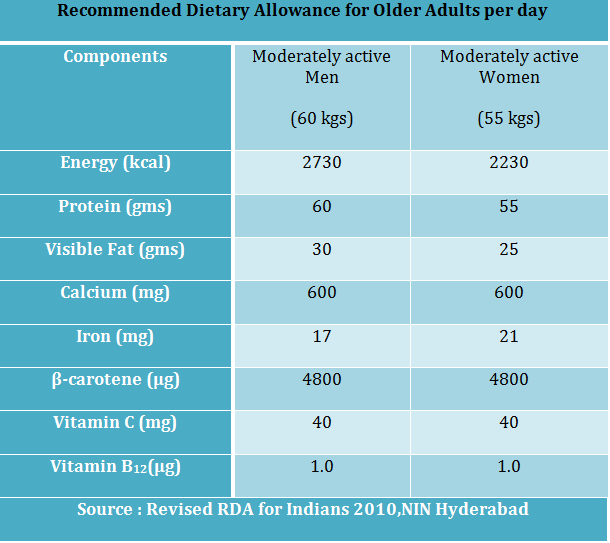
Older people are at higher risk of insufficient diet and lack of nutrition. Planning and preparing nutritious meals becomes more difficult with advancing age. Even though it is of high priority to consume more calcium, iron, fibre, protein and other nutrients, it can be hard to meet the dietary requirements due to physical, mental, economic, and social and lifestyle changes.
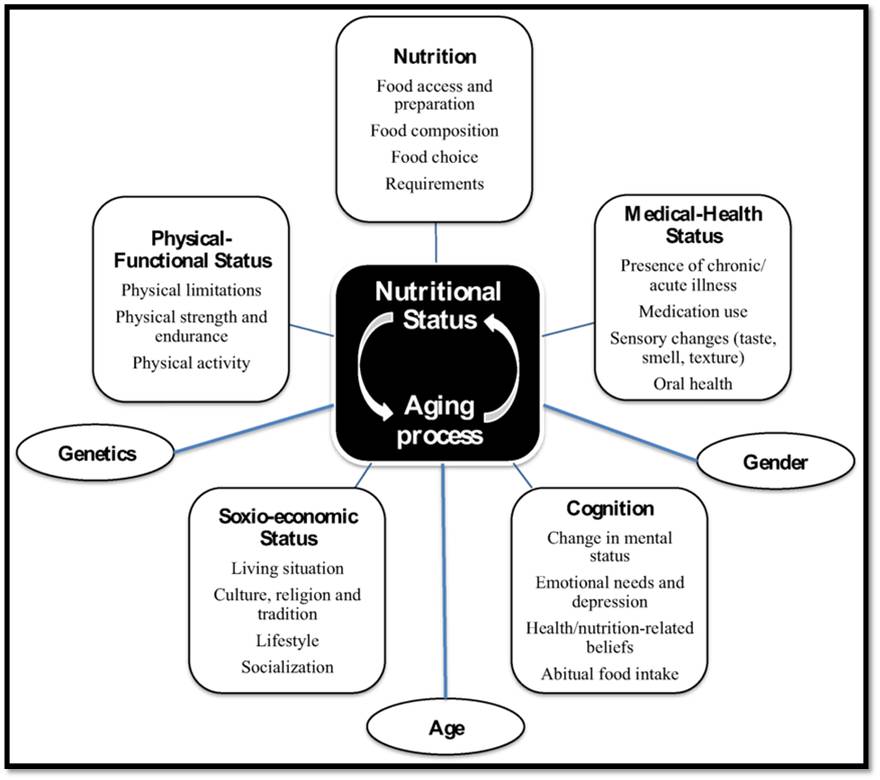
Medical factors:
With increasing age, we often come across health issues like breathing difficulties, joint pains, stroke, mood problems and poor memory. These conditions may affect one’s appetite, mobility or ability to swallow, all leading to altered food intake and suboptimal nutritional status. Medications can add to this due to the side effects of loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting, dry mouth, imperfect absorption of food and alterations in taste and smell. A heart-healthy diet is recommended for people of all ages, but it is especially important after midlife when the risk of heart disease is highest.
The ability to taste and smell food is an important part of feeling hungry and eating well. Foods may seem to lose their flavour as you age. Your favourite dishes might taste different. Older adults can experience diminished ability to taste and smell because of certain medications and conditions. Reduced ability to taste may also result from a decreased number of taste buds or receptors involved in the sensation of taste. The sense of smell also diminishes, particularly after age 70, perhaps due to loss of nerve endings in the nose. Loss of smell makes food less tasty and enjoyable.
Difficulty swallowing can result from a stroke or other conditions and lead to dietary deficiency if an appropriate alternative is not provided. The health of your teeth is an essential factor in your nutrition. Dental problems, poorly fitting artificial teeth or missing teeth make it difficult to chew. Improper chewing can lead to poor nutrition, reduced quality of life and diminished health in general.
Nutritional factors:
Many people don’t feel like eating and eat less as they age; making it difficult to get all the nutrients they need for good health. Changes in your body’s regulatory mechanism, hormonal balance and nervous stimuli can affect how much you eat. Your desire for food can also be affected by medications and other factors. Older adults may not absorb nutrients well because of age-related changes in metabolism (a collection of chemical reactions that takes place in the body’s cells). Vitamin B12 deficiency is particularly common because the digestive tract of an older adult doesn’t absorb this vitamin well, leading to depression and memory disorders.
Socio-economical factors:
Seniors living on fixed incomes may not be able to afford the amount of nutritious food needed to maintain good health. Money budgeted for groceries may take a back seat to the costs of utilities, housing, medication and health care. Eating alone can have a negative effect on your nutrition, especially if you are depressed or have a poor appetite. Older adults who live by themselves may also be vulnerable to social isolation, particularly if many of their life-long friends are no more.
Physical factors:
The ability to buy the ingredients and cook healthy meals are important factors in an elderly person’s nutrition. Homebound or disabled people are unable to go out grocery shopping or prepare meals thereby leading to poor health.
Psychological factors:
Very often, we fail to identify the emotional and psychological problems that can derail nutrition as we age. Depression is a common cause of weight loss and lack of proper nutrition in senior citizens. Stress and fearfulness can also cause you to eat less than you need. Alzheimer’s disease is the main cause of memory loss as we age. The onset of Alzheimer’s disease is insidious, and disease progression includes memory loss and loss of physical function and independence. Memory loss and confusion can affect an elderly person’s desire to eat and their ability to feed themselves.
If there is a problem there is a solution
Ways to approach the challenges of sub-optimal nutrition status:
Recognition of poor nutritional status is a key to reversing any effect. Prevention, early identification and treatment of weight loss are crucial to good health in the elderly.
The first step should always be to maximise an individual’s nutritional intake from regular food and drinks, often termed “Food First”. The Food First approach includes increasing the frequency of eating, maximising the nutrient and energy density of food and drinks and fortifying food with the much-needed nutritional elements.
Eating methods that ensure good nutrition:
- Encourage “little and often” – that is, three small meals with regular in-between snacks of energy-rich, high protein foods. Encourage people to eat every two to three hours
- Serve meals and snacks that are appealing in size and appearance – avoid large meals, use small plates and maximise the “eye appeal” of the food
- Drinks can reduce hunger – keep drinks for after meals rather than before and during a meal
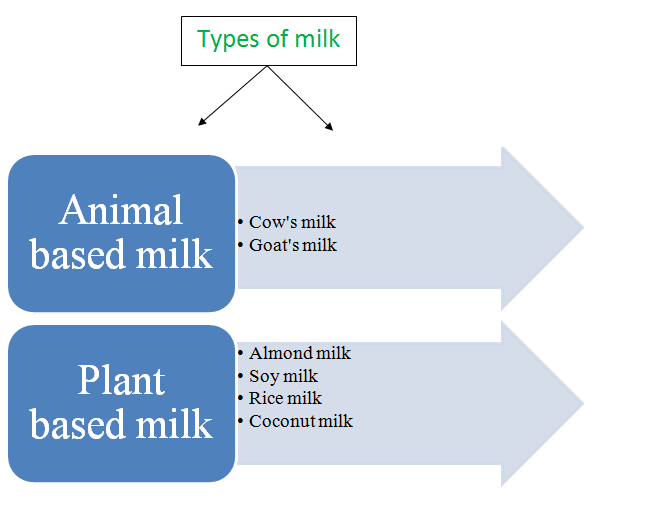
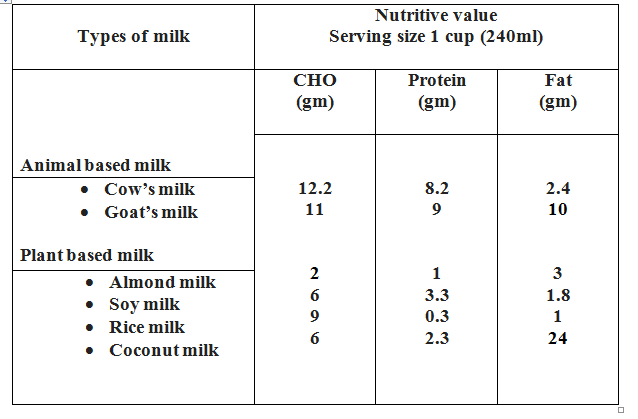
- Choose nourishing fluids – milk-based drinks, soups or fresh fruit juice can replace soda or coffee
- Consider meal settings – make mealtimes enjoyable and avoid interruptions or rushing during meals
- Find ways to stimulate hunger – a short walk before meals can be helpful
- Add flavour to your meals with herbs and spices
- Encourage adequate dental and oral care
- Modify the consistency and texture of foods as needed instead of leaving them out; try soft foods that require little chewing eg. tender cuts of meat cooked in gravies are often more easily managed
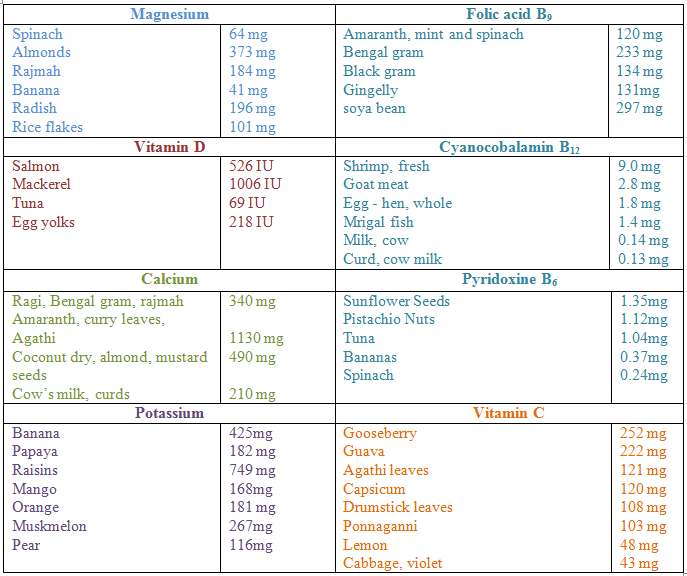
- Consuming a variety of foods from the four food groups that include grains, grams, fruits and vegetables will ensure that energy, macronutrient and micronutrient requirements are met
- Food is the best way to get the nutrients you need; dietary supplements like vitamin and mineral pills may be prescribed if you have deficiencies due to improper absorption of certain nutrients but not otherwise
Healthy ageing recommendations: If you follow a few tips on healthy eating as you age, your risk of disease can be largely minimized:
- maintain a healthy weight and body composition
- increase vegetable and fruit consumption
- reduce total, saturated and trans fat consumption
- increase dietary fibre
- reduce dietary sodium (salt) and increase dietary potassium
- obtain your vitamins and minerals from foods rather than supplements
- maintain normal blood cholesterol, blood glucose and blood pressure
- limit alcohol intake; stay away from tobacco in any form
- increase physical activity
- A heart-healthy diet that limits saturated fat and salt, while incorporating whole grains, plenty of fruits and veggies and walnuts, almonds, avocados, olive or canola oil and potassium-rich foods, such as bananas and low-fat milk is best suitable for senior citizens. Calories from fats should be limited to between 20 and 35 percent of an older adult’s diet and most of the fats should be unsaturated (namely nuts, vegetable oils and oily fish are rich in unsaturated fats).
Don’t hesitate to ask for support:
- Use convenience foods: ready to make cereals like bread, cornflakes, oats, adai using organic millets etc
- Enlist family and carer support; consider a service that delivers prepared meals to your home. It minimises your efforts and is usually affordable
- Prepare snacks and meals to eat later if you’re unable to prepare each meal
- Add extra nutrients to meals and snacks to boost energy intake, for example, add soya paneer to gravies and powdered peanuts to vegetable dishes
- Ensure shopping and food preparation assistance is available
- Consider assessment by a physiotherapist or occupational therapist
Make eating a social event:
Meals are more enjoyable when you eat with others. Find a meal program for seniors by contacting your local senior centre, attend an adult day-care centre or invite friends, family and neighbours to share meals with you. There are many ways to make mealtimes pleasing.
Nutrition education programs to improve mental health:
Nutrition education programs for the caregivers of people with poor mental health are the best way to prevent weight loss and improve their nutrition status. The most recent collective evidence suggests that the optimal approach for Alzheimer’s disease would seem to combine early nutritional approaches (multi-vitamin supplements), along with lifestyle modifications such as social activity and mental and physical exercise, with an addition of medicines if necessary.
Our Upcoming Program for Seniors:
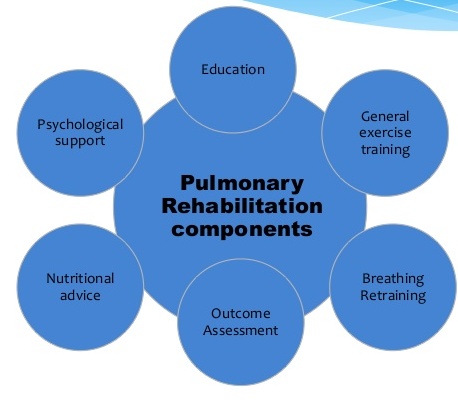
As part of our heart-health awareness campaign, Cardiac Wellness Institute is launching a program for senior citizens (men and women 60 years of age and older) to enlighten and equip them with skills for ageing healthily. The Healthy Aging program will commence with a free introductory session from 10.30 am -12.30 pm on Wednesday, 22nd November 2017. Thereafter, interested seniors can enrol for weekly sessions. The components included in the program are Doctor Consultation, Exercise Sessions, Nutrition Advice, Group Education and Counseling.
Registration is mandatory and free of cost. Please call +9144 43192828 or +91 9940408828 or send an email to info@cardiacwellnessinstitute.com for registration.
Active ageing benefits the individual, improves health, increases independence and assures a good quality of life.

 programs for individuals of different ages and walks of life, it is part of my work to address their questions and concerns related to exercise. In this blog post, I hope to clarify some of the doubts pertaining to exercise in the minds of patients who have undergone or are planning to go through a cardiac surgery.
programs for individuals of different ages and walks of life, it is part of my work to address their questions and concerns related to exercise. In this blog post, I hope to clarify some of the doubts pertaining to exercise in the minds of patients who have undergone or are planning to go through a cardiac surgery.